Integrating Coding, Marking, and Labeling Equipment with Bagging Machines
A Comprehensive Guide for OEMs and Manufacturers

Marc Discher
Global Marketing Manager OEM
Topics: Bagging machines, Integrate coding and bagging machines
Introduction
The modern packaging industry demands more than just efficient bagging operations—it requires comprehensive solutions that help ensure product traceability, regulatory compliance, and supply chain visibility. For OEMs and manufacturers utilizing bagging systems, integrating coding, marking, and labeling equipment has become essential for meeting regulatory requirements, enhancing brand protection, and optimizing operational efficiency. When executed properly and with the support of coding equipment suppliers, this integration process can significantly improve production line performance while reducing operational costs.
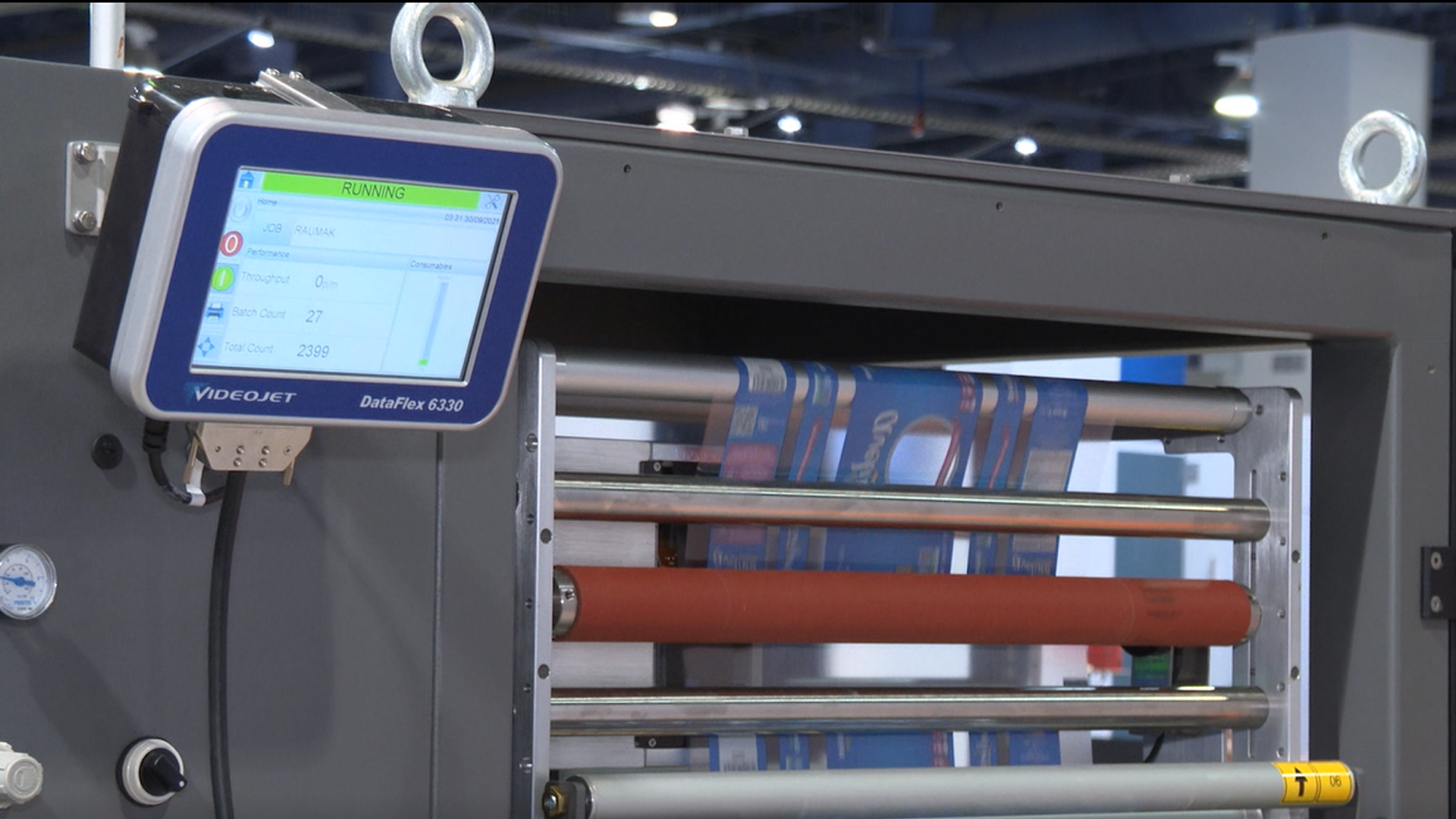

Understanding Bagging Machine Technologies
Primary Bagging System Types
Modern bagging operations employ several distinct machine configurations, each with unique integration requirements for coding and marking equipment:

Vertical form fill seal (VFFS) machines
Vertical form fill seal (VFFS) machines create bags from rolls of film, forming them around a tube before filling and sealing. These machines are particularly suitable for powders, granules, and small products, offering high-speed operation with the flexibility to create various bag styles including pillow bags and quad-seal designs.

Horizontal form fill seal (HFFS) machines
Horizontal form fill seal (HFFS) machines operate by unwinding film horizontally, forming pouches through a continuous tube process, then filling and sealing products. HFFS systems excel in handling solid products, pastes, and items requiring gentle handling during the packaging process.

Pre-made pouch filling machines
Pre-made pouch filling machines work with pre-manufactured pouches, offering maximum flexibility for complex bag designs including stand-up pouches, zipper bags, and specialized shapes. These systems can achieve speeds up to 100 bags per minute in dual-configuration setups while maintaining precise filling accuracy.

Open-mouth bagging systems
Open-mouth bagging systems are designed for handling larger package sizes, typically ranging from 5 to 50 kg per bag, and are ideal for granular or other free-flowing materials in industries such as food, chemicals, and minerals. These systems can process up to 600 bags per hour while maintaining precise weight control.
Coding and Marking Technologies for Bagging Applications
Thermal Transfer Overprinting (TTO)
Thermal Transfer Overprinting is an ideal coding solution for flexible packaging. TTO technology utilizes a thermal printhead and wax-resin or resin ribbons to create high-resolution 300 dpi print quality directly onto flexible substrates. This technology is particularly effective for printing on flat, thin, flexible films before bag formation, allowing the printed film to be formed into various bag types including zipper, four-sided, gusseted, and stand-up pouches.
The key advantages of TTO include solvent-free printing, optimal durability for industrial applications, and the ability to print variable content in real-time at high speeds. TTO systems can accommodate various flexible substrates including plastics, foils, films, and low-density polyethylene materials.
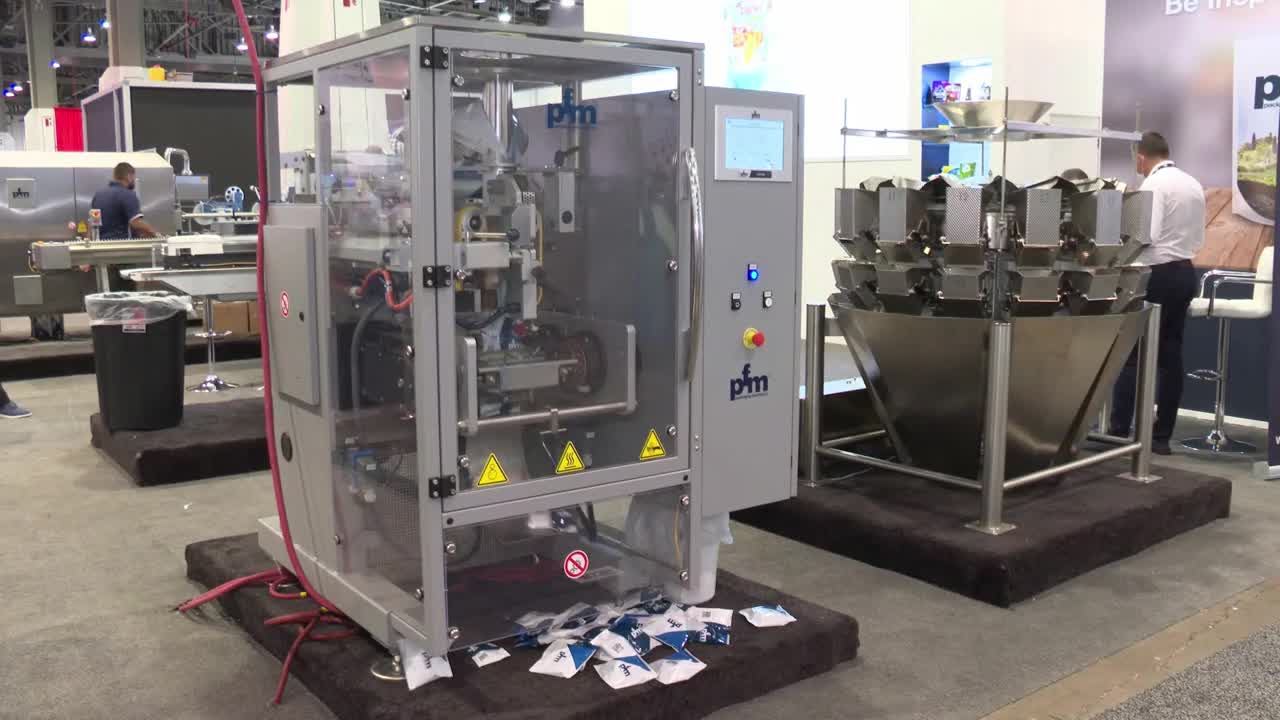

Continuous Inkjet (CIJ)
Continuous inkjet printers offer non-contact printing for applying codes and messages on virtually any substrate, including flat or curved surfaces. CIJ technology operates by breaking a continuous stream of ink into droplets, then applying static electric charges to the droplets, directing them to form characters in a grid pattern. These systems can print at speeds up to 508 meters per minute and work effectively with plastic, glass, metal, film, and paper packaging materials.
CIJ printers are commonly used for printing expiry dates, batch numbers, serial numbers, barcodes, logos, and promotional codes. The technology’s flexibility and reliability make it ideal for industrial coding applications where consistent performance is critical.
Laser Marking Systems
Laser technology provides superior precision and sustainability for bag marking applications. Advanced laser systems deliver high-quality, permanent marks without requiring consumables like inks, labels, or dies. This technology eliminates maintenance costs associated with traditional ink-based and mechanical labeling systems while providing exceptional accuracy and mark quality.
Print and Apply Labeling (LPA)
Print and apply systems automatically create labels with variable data, such as shipping information, and then immediately apply the label to a product, case, or pallet. These systems help ensure accurate labeling and placement by scanning containers as they travel down conveyors, printing corresponding labels with the unique information, and firmly applying labels as containers pass by the machine.
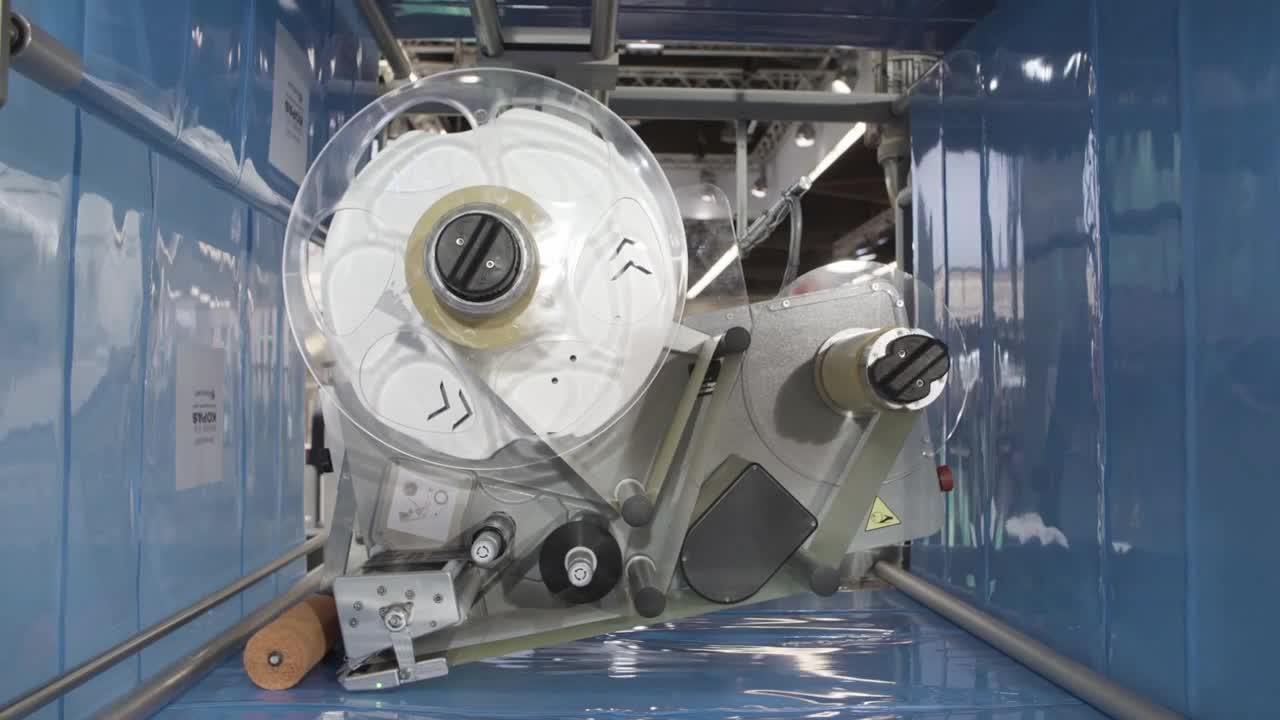
Integration Strategies and Best Practices
Compatibility Assessment and Planning
Successful integration begins with a comprehensive compatibility assessment. Manufacturers should evaluate their specific production line requirements, including materials being marked, surface textures, production speeds, and available space constraints. This assessment should consider both current needs and future requirements to ensure the coding equipment can accommodate increasing production volumes without significant disruption.
Integration Assessment
Get in touch with our expert sales engineers for a free integration assessment.
Contact Us

Placement and Mounting Considerations
Optimal placement of coding and marking equipment is crucial for successful integration. The equipment needs to align with the packaging process without impacting other operations, while maintaining accessibility for quick service and maintenance. Proper mounting using appropriate brackets helps ensure optimal positioning and stability during high-speed operations.
Control System Integration
Modern bagging systems utilize PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems for precise control and coordination. Successful integration requires connecting the coding equipment to the machinery’s control system, allowing for seamless operation within existing setups. This integration allows for synchronized operation between bagging and coding processes, helping ensure consistent code placement and quality.
Software Configuration and Setup
Proper software configuration is essential for optimal performance. This includes installing and configuring necessary software to control printing parameters such as font size, message content, and print speed. The software setup should accommodate variable data code content requirements including lot codes, expiration dates, and batch numbers.
Overcoming Integration Challenges
Technical Integration Hurdles
Manufacturing facilities may face significant challenges when integrating new coding systems with an existing bagging unit. Previous generation systems can present particular difficulties, as older technologies could require upgrades to facilitate smooth integration with modern coding equipment. The most effective approach involves working closely with coding equipment suppliers to assess the existing infrastructure and propose upgrades that minimize disruption.
Operational Considerations
Dust and environmental pollution common in bagging operations create additional challenges for coding equipment. Temperature fluctuations, vibration, and uneven package shapes require coding solutions that can withstand unfavorable conditions while maintaining consistent mark quality. Proper equipment selection needs to take these environmental factors into account to help ensure reliable long-term performance.
Cost and ROI Analysis
The initial capital investment for automated coding and marking systems can be substantial, particularly for smaller businesses. However, comprehensive ROI analysis often demonstrates significant long-term benefits.
The basic ROI formula for equipment integration is: ROI = (Revenue – cost of equipment – operating costs)/(Cost of equipment) x 100. Manufacturers should consider not only initial purchase costs, but also ongoing operational expenses including maintenance, consumables, and training.

Request Custom ROI Analysis
Get expert help with your ROI analysis on your coding equipment.
Contact Us
Partnership Models with Coding Equipment Manufacturers
OEM Partnership Benefits
Strategic partnerships with coding technology manufacturers can provide significant advantages for bagging equipment OEMs. These collaborations help enable companies to focus on their core competencies while leveraging specialized coding expertise to deliver comprehensive solutions. OEM partnerships can drive innovation, reduce development costs, and expand market reach by combining complementary technologies.
Collaborative Engineering Approach
Leading coding equipment manufacturers typically offer engineer-to-engineer collaboration, providing detailed drawings, documentation, and product testing support. This collaborative approach helps ensure no design aspect is overlooked and allows for equipment to be targeted to specific applications based on material handling requirements. The partnership model enables customization for available space, production constraints, plant specifications, and speed requirements.
Training and Support Programs
Comprehensive training programs are essential for successful integration. Effective partnerships include thorough operator training, ensuring personnel can confidently operate and troubleshoot coding equipment. Support programs should encompass maintenance planning, technical support availability, and spare parts accessibility.
Optimize Your Integration
Partner with our coding and marking specialists for seamless equipment integration, customized solutions, and expert training. Contact us today to boost your production efficiency and innovation.
Contact Us

Implementation Best Practices
Pre-Implementation Planning
Successful implementation requires thorough planning that considers production line integration, workflow optimization, and staff training requirements. Manufacturers should establish clear project timelines, define success metrics, and allocate appropriate resources for installation and testing phases.
Testing and Validation
Comprehensive testing protocols help ensure the coding equipment functions seamlessly inside bagging operations. This includes alignment verification, print quality assessment, speed synchronization testing, and integration validation with existing control systems. Testing should encompass various operating conditions to ensure consistent performance across production requirements.
Maintenance and Optimization
Long-term success depends on proper maintenance planning and continuous optimization. Regular calibration, consumable replacement schedules, and performance monitoring help maintain optimal coding quality and minimize downtime. Automated monitoring systems can identify potential issues with coding equipment before production is impacted.
Future Considerations and Technology Trends
Automation and Smart Manufacturing
The integration of coding and marking equipment with bagging machines is evolving toward greater automation and smart manufacturing capabilities. Modern systems often incorporate vision verification, barcode readers, and reject systems to help ensure product quality and compliance. These automated features reduce manual intervention requirements while improving overall system performance.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Environmental considerations increasingly influence equipment selection decisions. Laser marking systems significantly reduce consumable requirements, minimizing environmental impact and lowering ongoing operational costs. Manufacturers are prioritizing technologies that reduce waste generation while maintaining high-quality marking capabilities.
Scalability and Flexibility
Future-focused integration strategies emphasize scalability and flexibility to accommodate changing market demands. Modular system designs allow for capacity expansion and technology upgrades without requiring replacement of the entire system. This approach protects long-term investment while enabling adaptation to evolving production requirements.
Conclusion
Integrating coding, marking, and labeling systems with bagging equipment represents a critical step toward optimized packaging operations. Success requires careful technology selection, thorough compatibility assessment, and strategic partnership with experienced coding equipment suppliers. While initial implementation may present challenges, long-term benefits such as improved efficiency, regulatory compliance, and cost reduction help justify the investment.
OEMs and manufacturers who approach integration systematically, leveraging manufacturer expertise and following established best practices, can achieve significant competitive advantages in today’s demanding production environment. The key lies in viewing coding equipment integration not as an additional complexity, but as an essential component of modern, efficient packaging operations.
Marc Discher is a marketing leader at Videojet Technologies with extensive experience supporting OEMs in integrating coding and marking solutions into production lines. He specializes in aligning technology with complex manufacturing needs, helping global partners improve efficiency and compliance.
